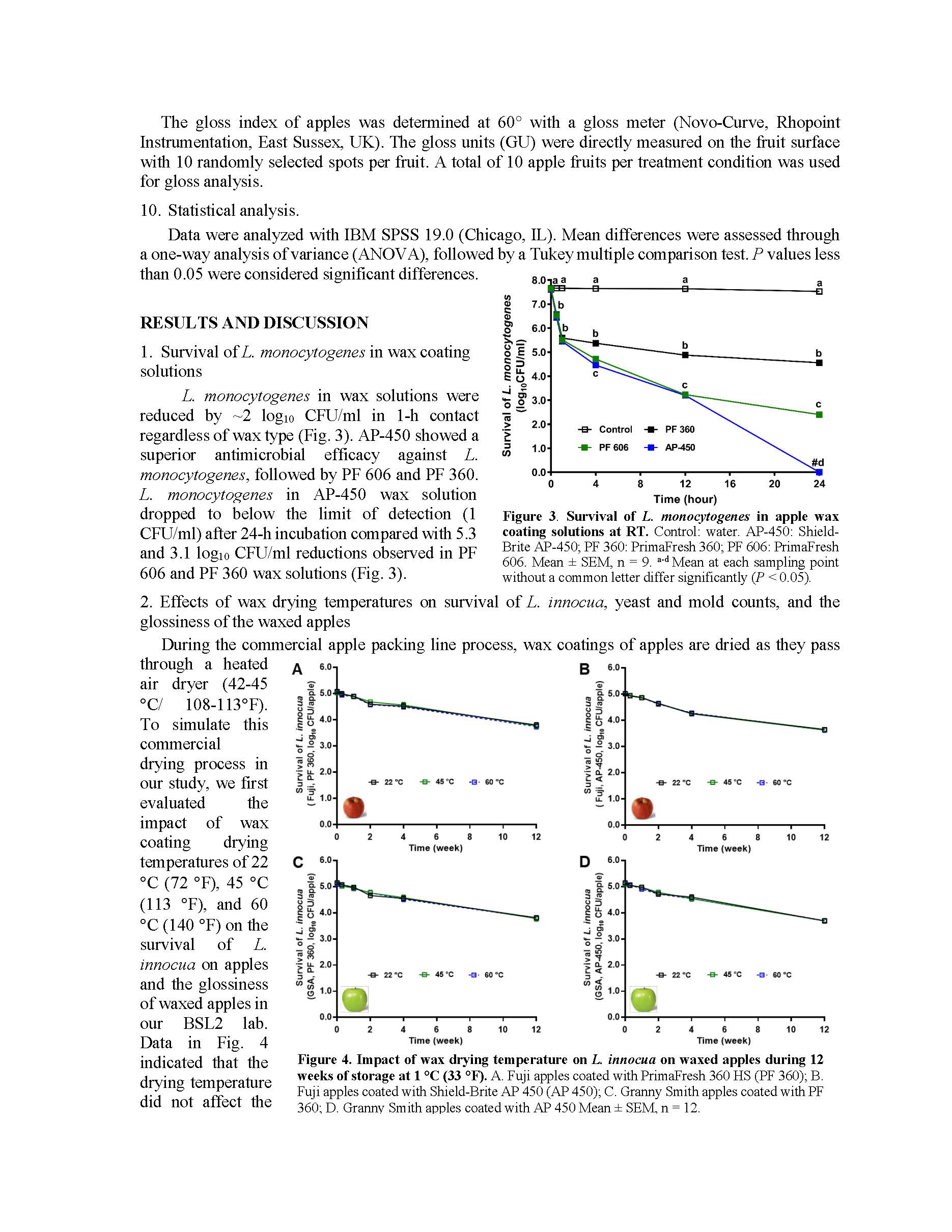
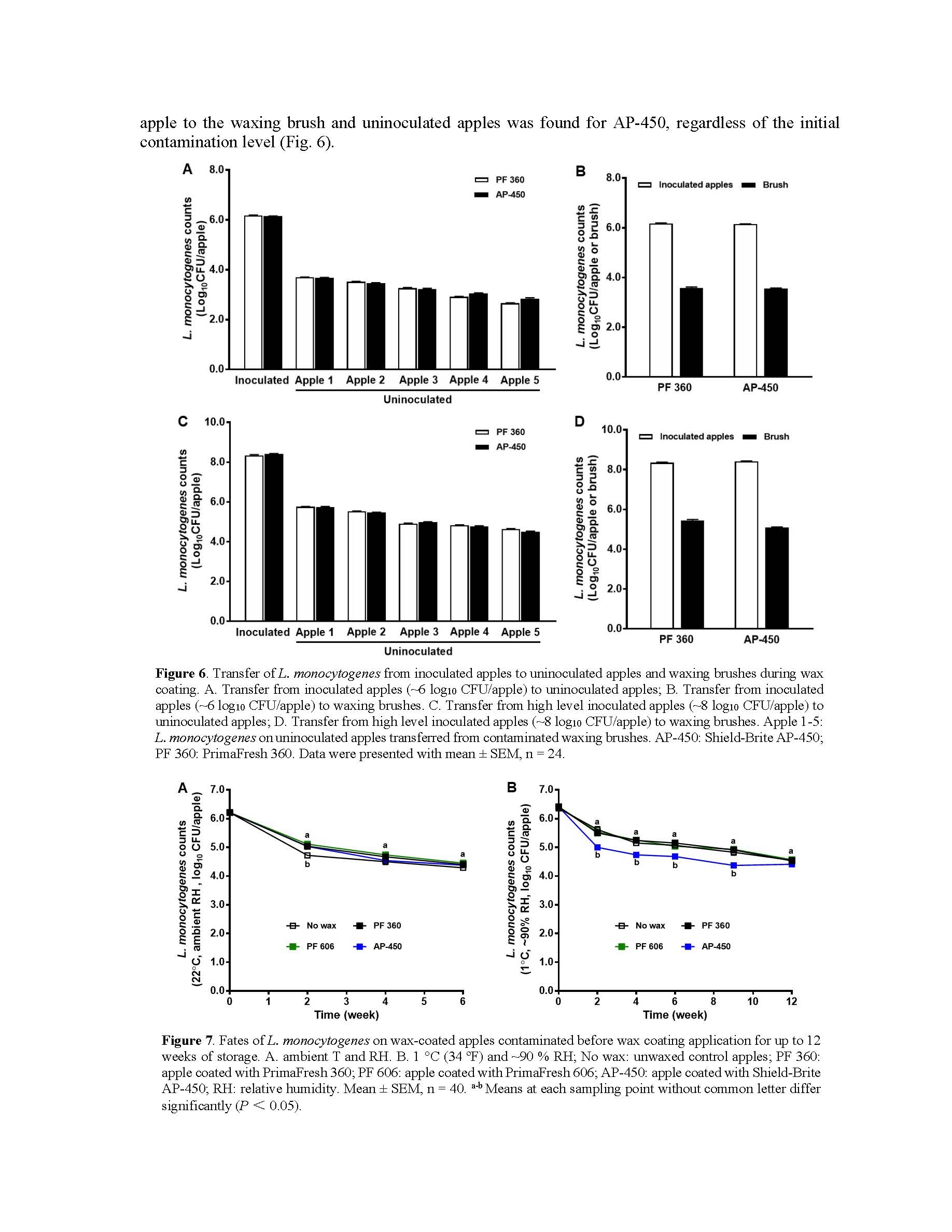
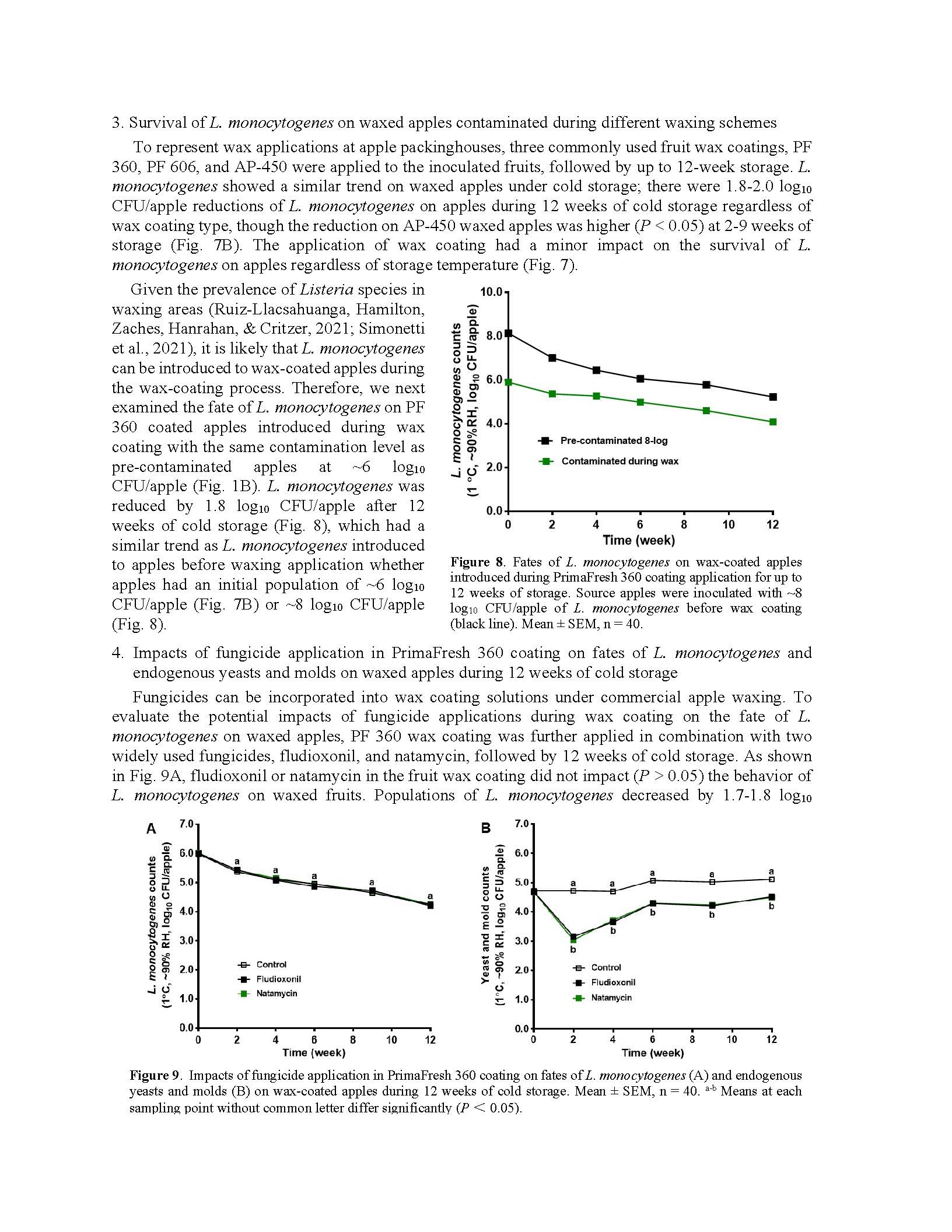
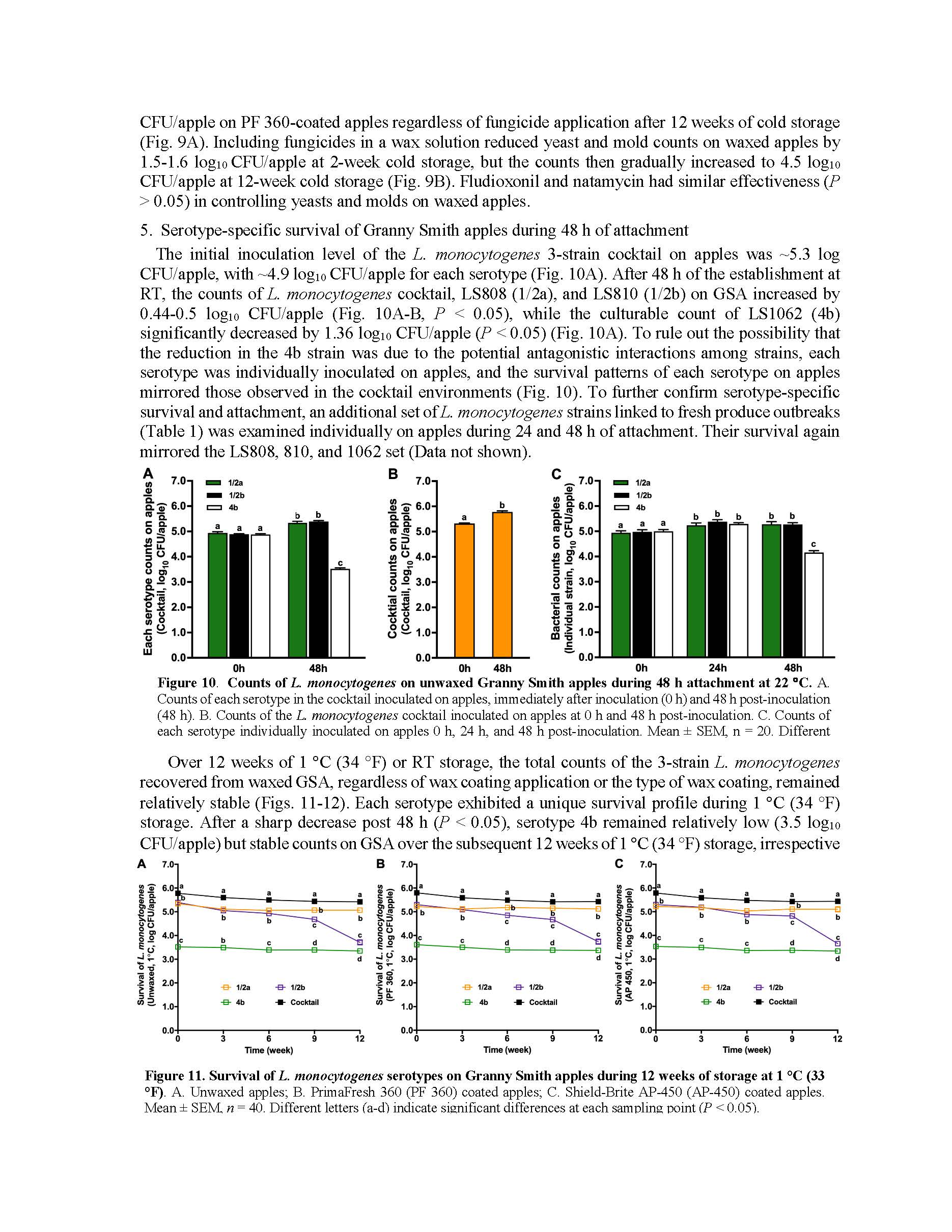
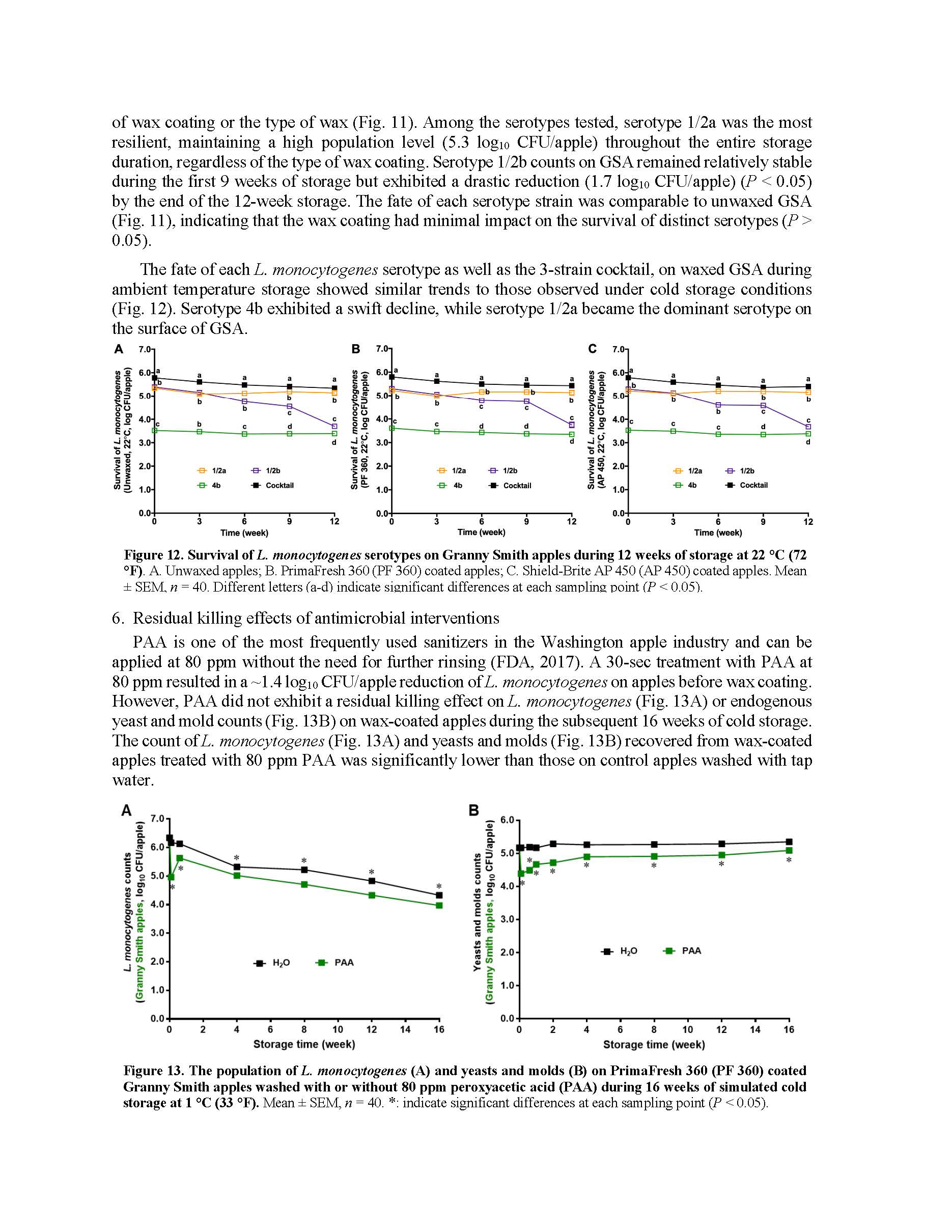
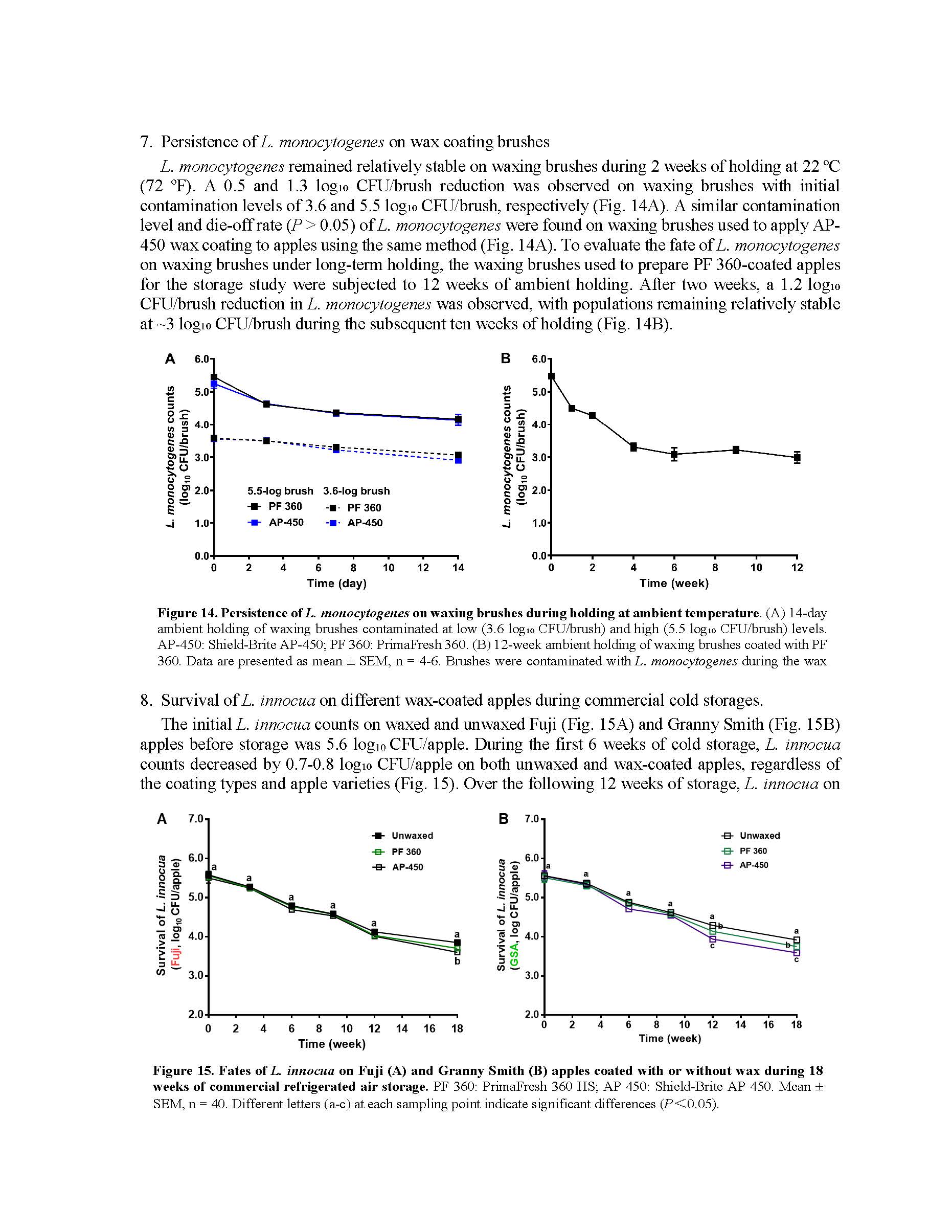
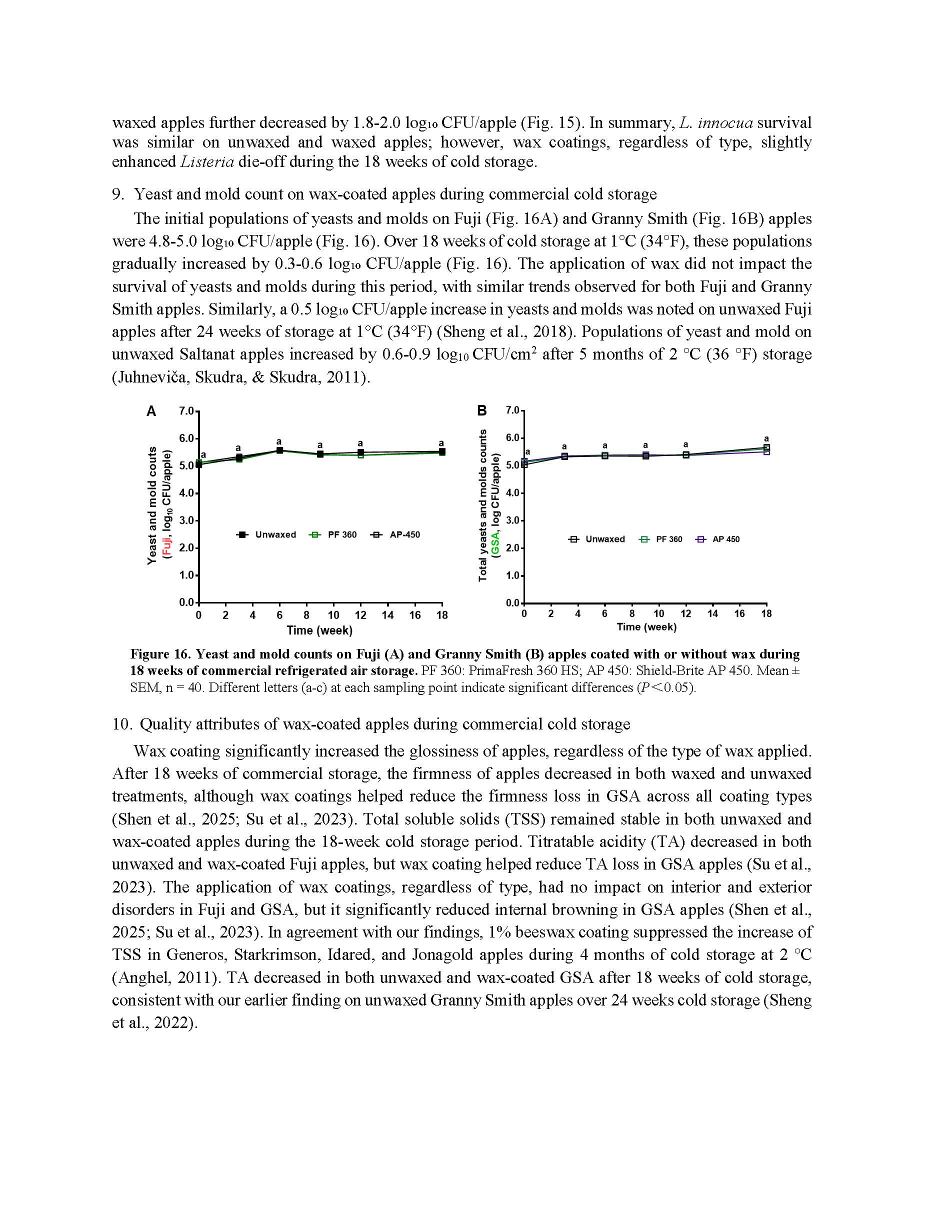
Fate of Listeria on fresh apples as affected by commercial apple waxes
Author: Meijun Zhu
Published: 2025
Summary: This research examines the fate of Listeria monocytogenes on apples contaminated before and during wax coating, its persistence on contaminated waxing brushes, cross-contamination risks, and the serotype-specific survival of L. monocytogenes on wax-coated apples. The study further investigates the fate of Listeria and resident yeasts and molds on apples treated with commercial wax under cold storage, using Listeria innocua as a surrogate. Findings indicate that while wax coatings enhance apple glossiness, help maintain weight, and slightly reduce firmness loss, they offer limited antimicrobial effects against Listeria. Specifically, a reduction of about 1.9 log₁₀ CFU/apple was observed over 18 weeks of commercial refrigerated air storage - comparable to that on unwaxed apples. The survival dynamics of L. monocytogenes also varied by serotype, with serotype 1/2a exhibiting higher resilience than others, such as serotype 4b, which declined more rapidly. There was also a notable cross-contamination risk among contaminated apples, uncontaminated apples, and waxing brushes during the simulated waxing process. L. monocytogenes remained viable on waxing brushes for up to 12 weeks at ambient temperature, with an initial 1.2 log₁₀ CFU/brush reduction in the first two weeks, followed by stable populations at ~3 log₁₀ CFU/brush during the subsequent ten weeks of holding. Additionally, the wax coating did not impact the survival of yeasts and molds on apples, with an increase of 0.4–0.5 log₁₀ CFU/apple observed after 18 weeks of cold storage, regardless of wax type. Including fungicides in the wax coating effectively reduced yeasts and molds on wax-coated apples; however, it did not impact L. monocytogenes survival. Overall, this research underscores that while wax coatings offer some benefits for fruit quality, they are insufficient for controlling Listeria contamination risks during apple storage and pose a cross-contamination risk during the waxing process. The findings highlight the need for enhanced sanitation strategies and the development of wax coatings with antimicrobial properties.
Keywords: