Feeding stimulants to increase efficacy of insecticides
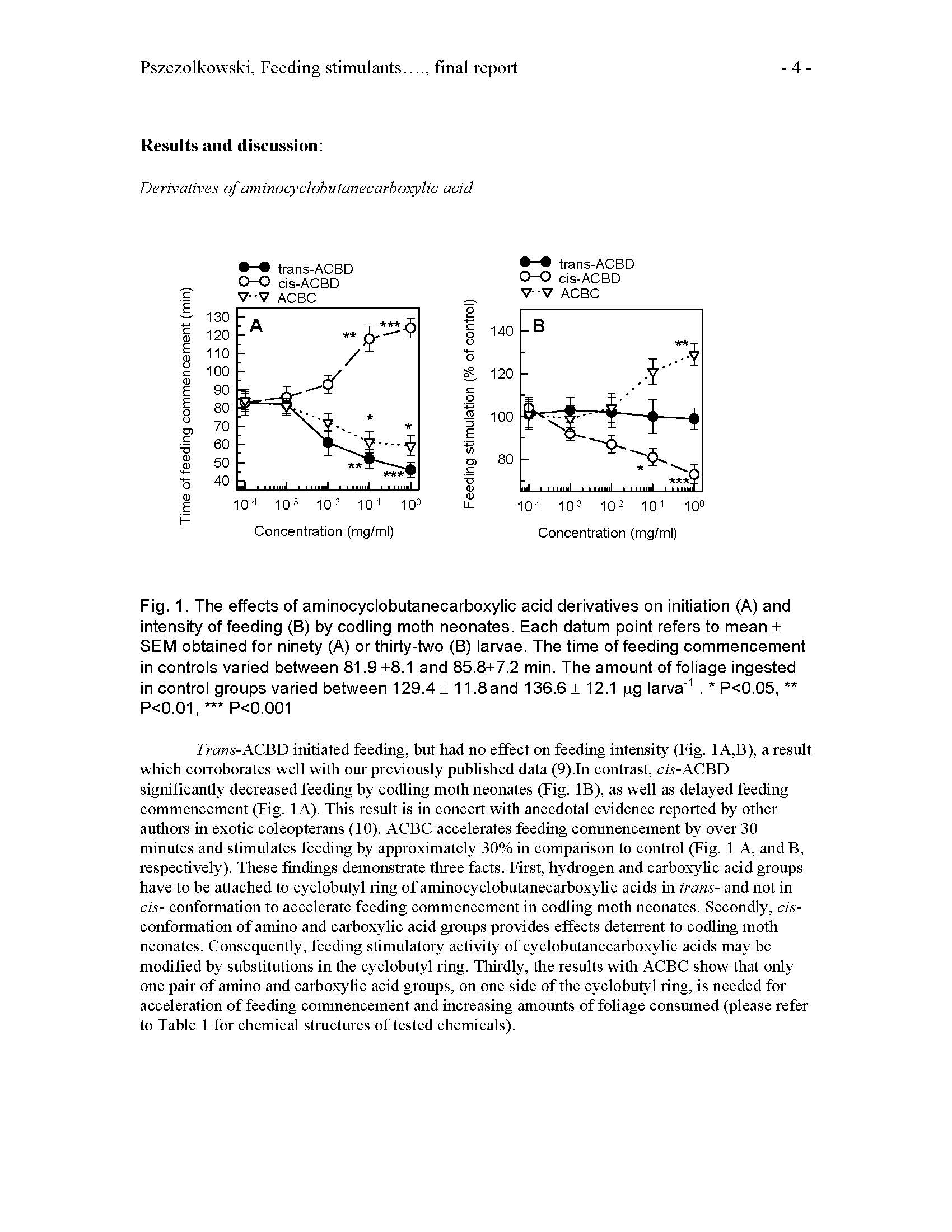
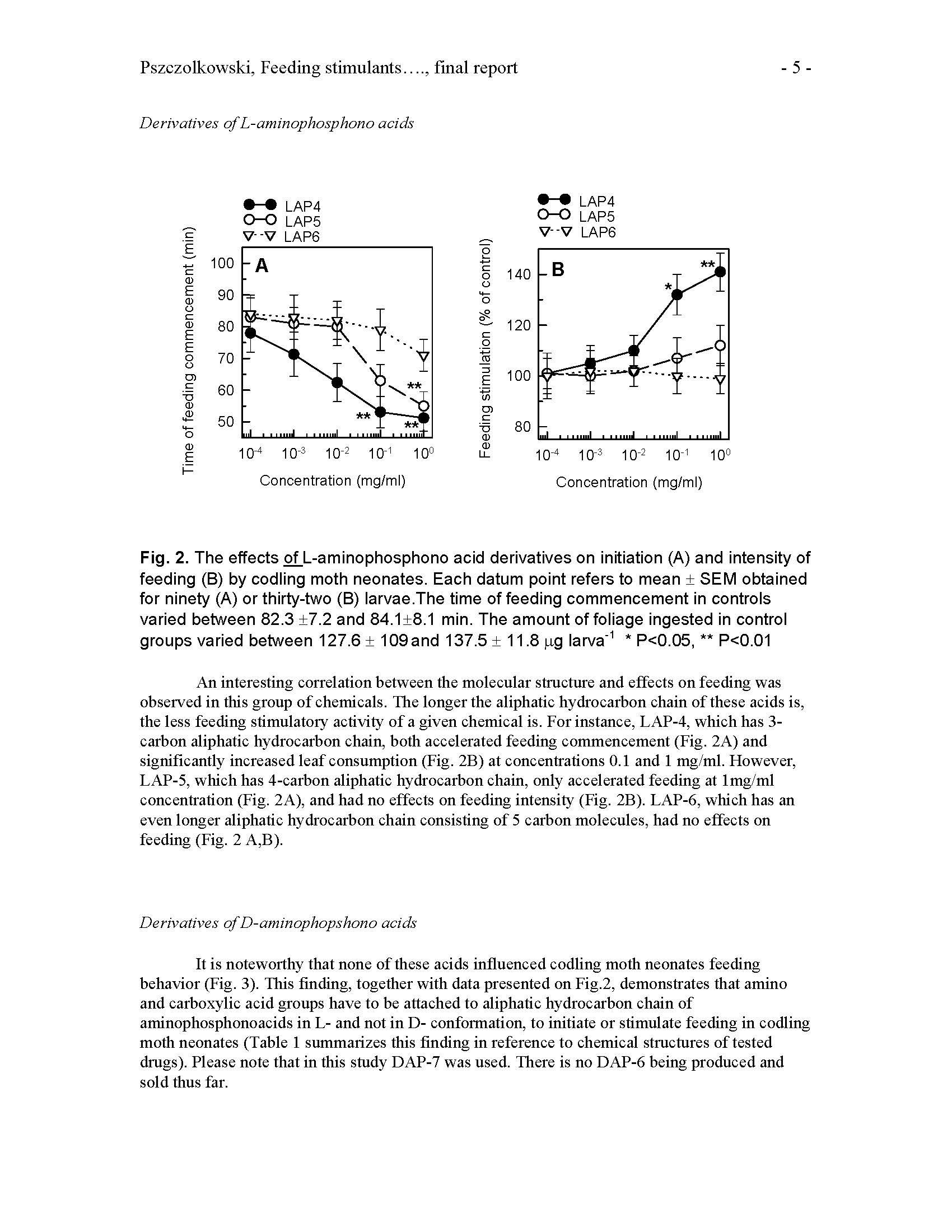
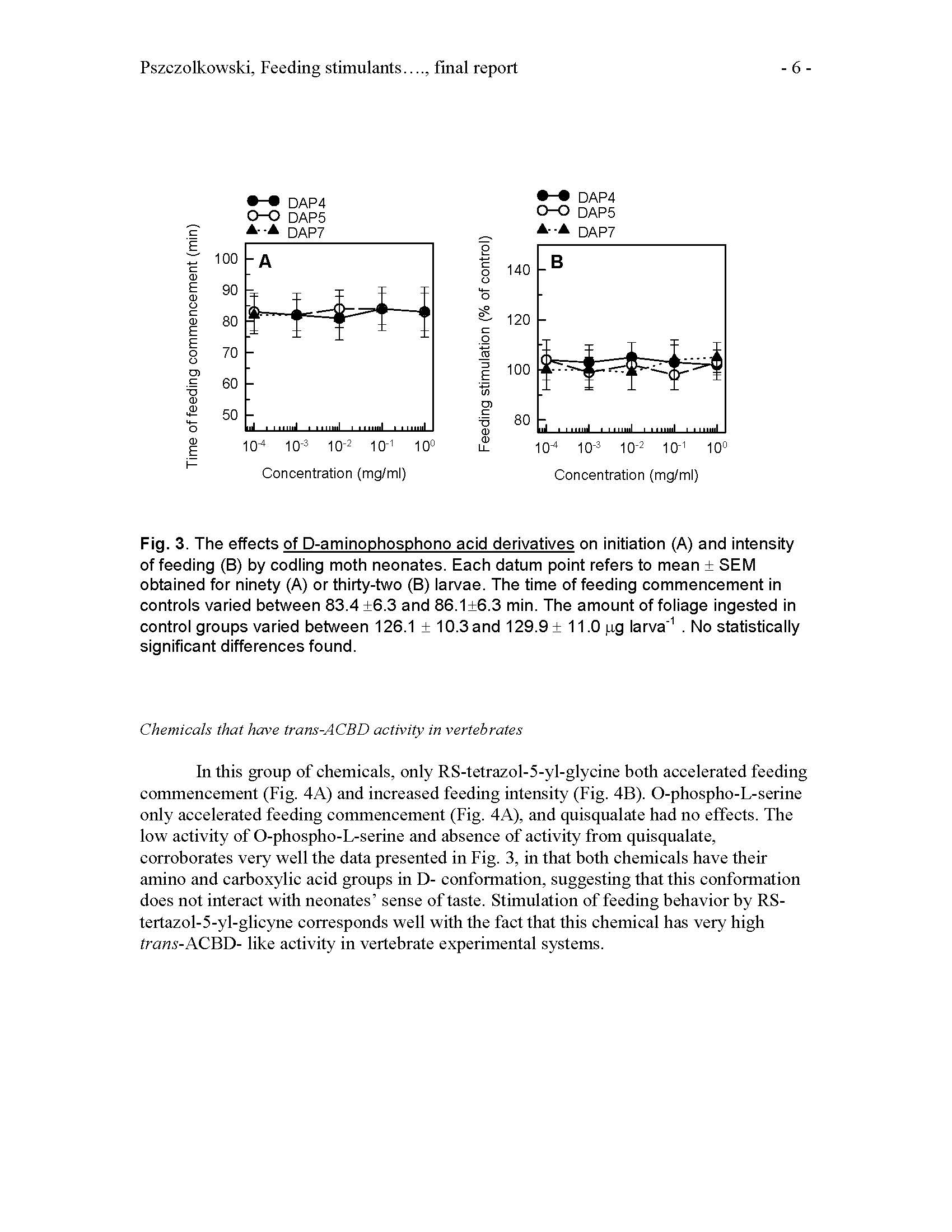
Author: Maciej A. Pszczolkowski
Published: 2005
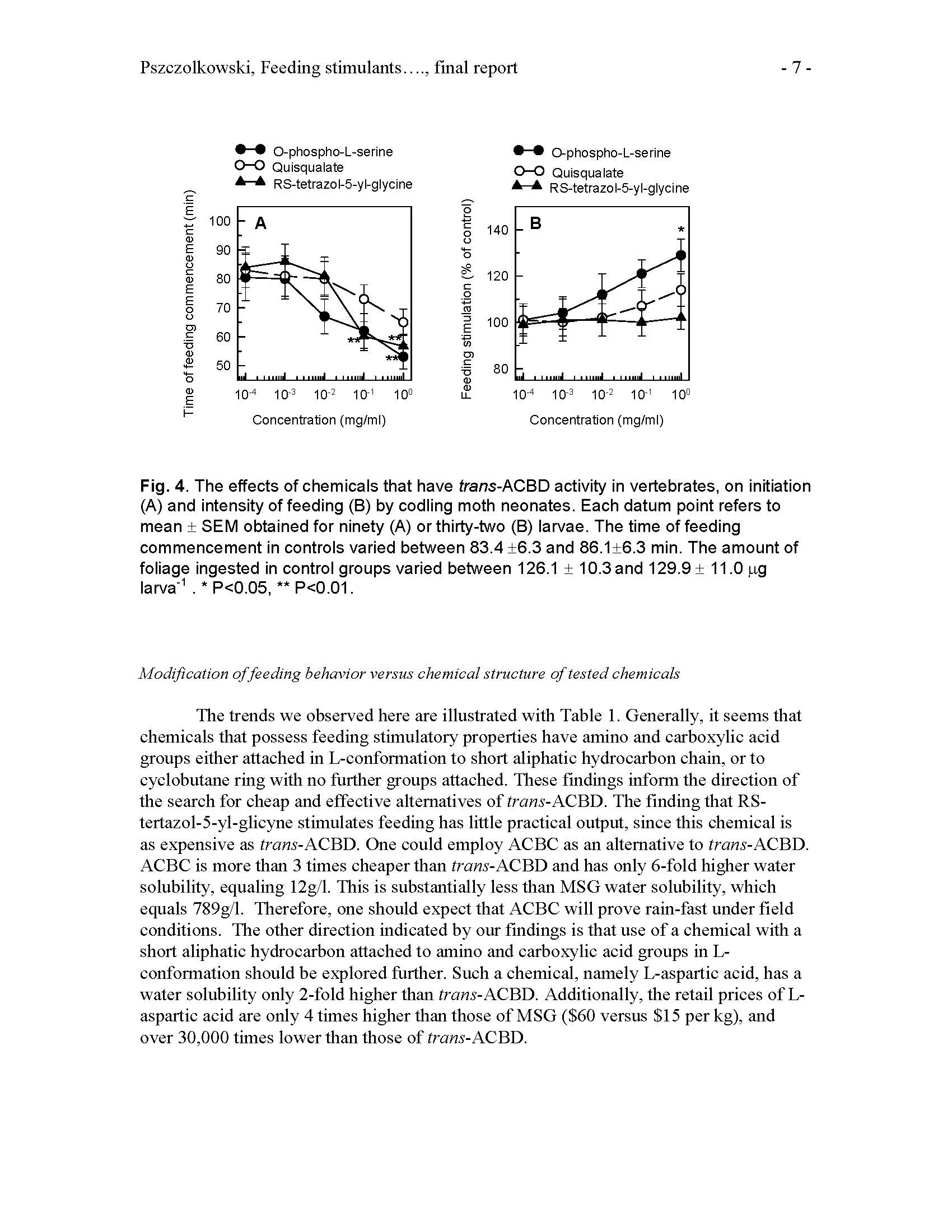
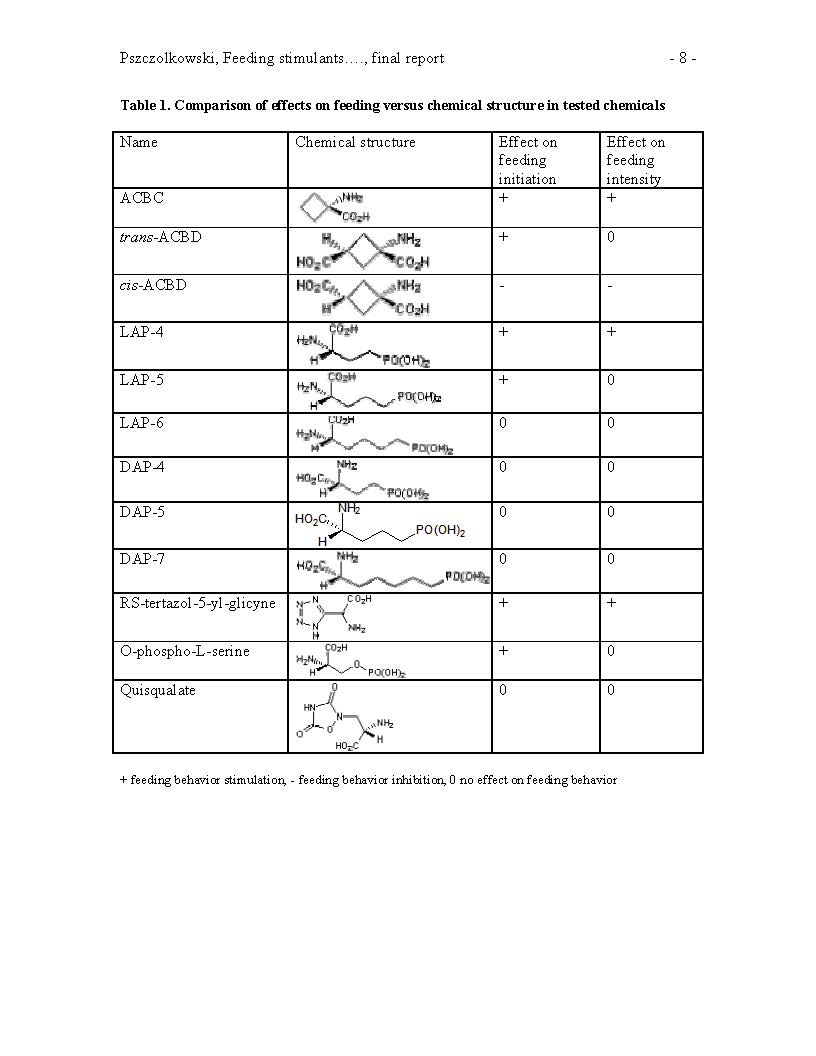
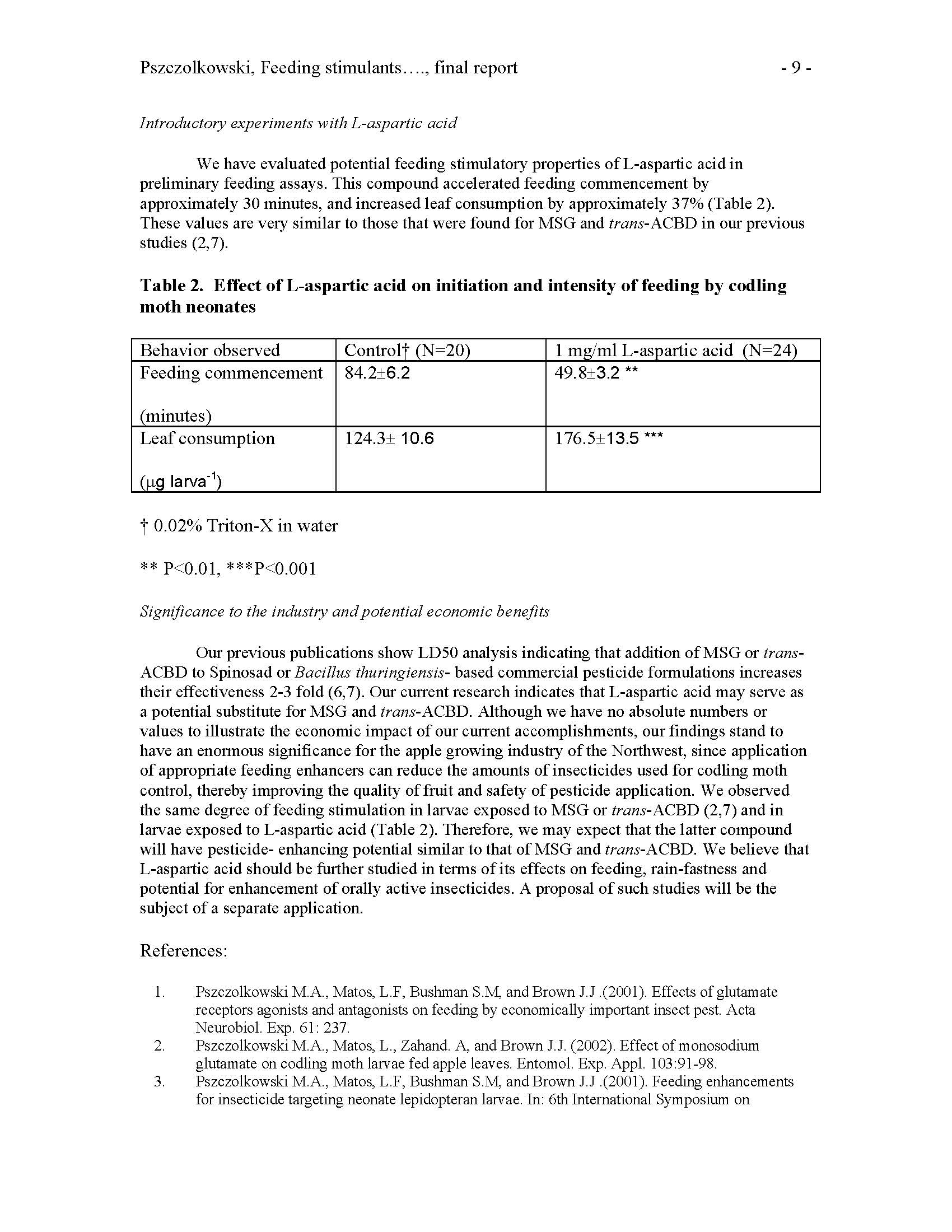
Summary: The studies previously done and published by PI and Co-PI in codling moth neonates (1,2) indicated that monosodium glutamate (MSG) stimulates feeding in neonates of this species. Therefore MSG can be successfully used for enhancement of insecticide formulations by either increasing their efficacy and/or maintaining their efficacy at reduced toxic ingredient amounts (3- 6). MSG is moderately rain-fast, however (5). To solve the problem of moderate MSG rainfastness, PI and Co-PI suggested use of trans-1-aminocyclobutane-1,3- dicarboxylic acid (trans- ACBD). trans-ACBD has superior rain-fastness, and feeding stimulatory and pesticide enhancing properties (7), however it is difficult to synthesize, and expensive because of its low-scale production for laboratory use only. The general objective of this project was to design or suggest another chemical substance that has feeding stimulatory properties similar to monosodium glutamate, but is cheaper than trans-ACBD.
Keywords: