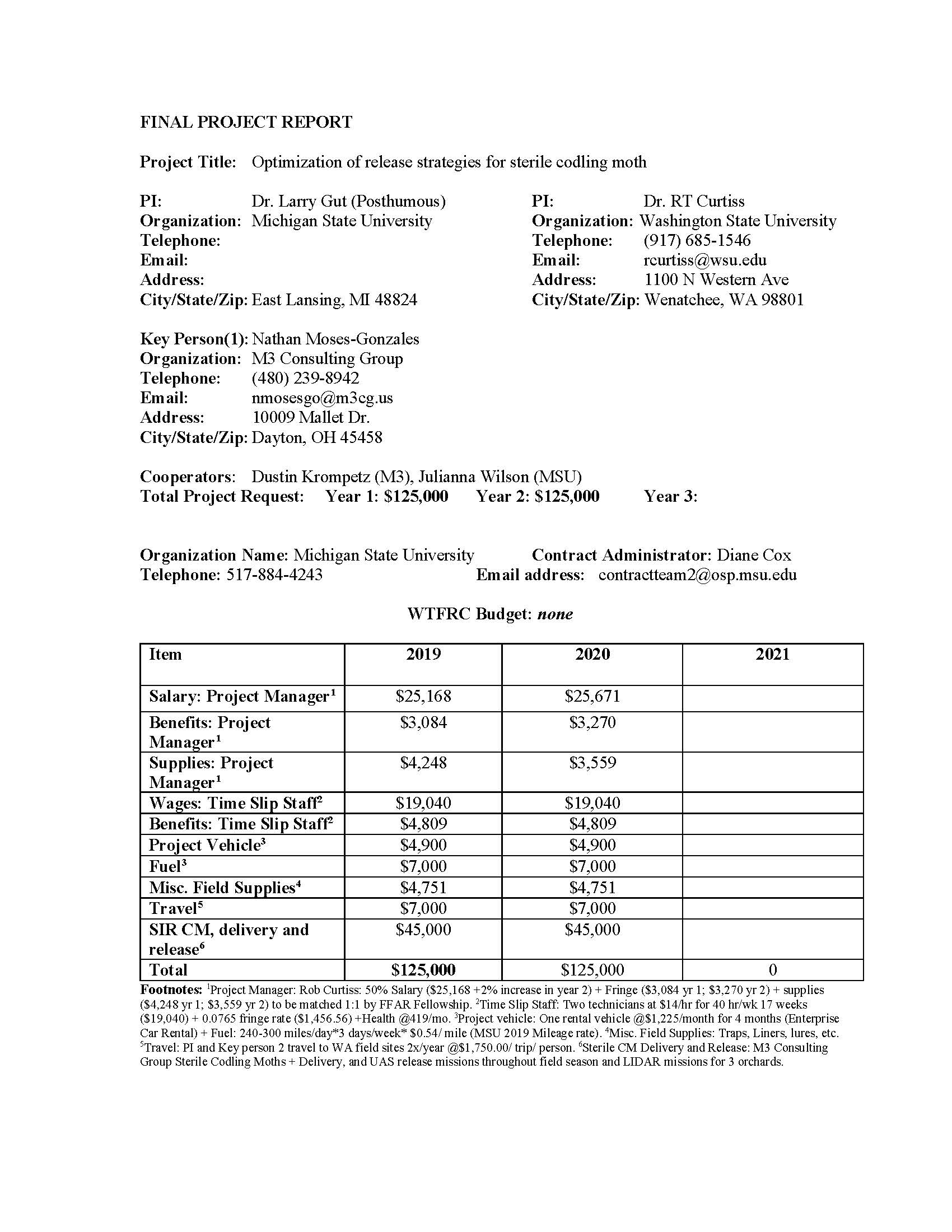
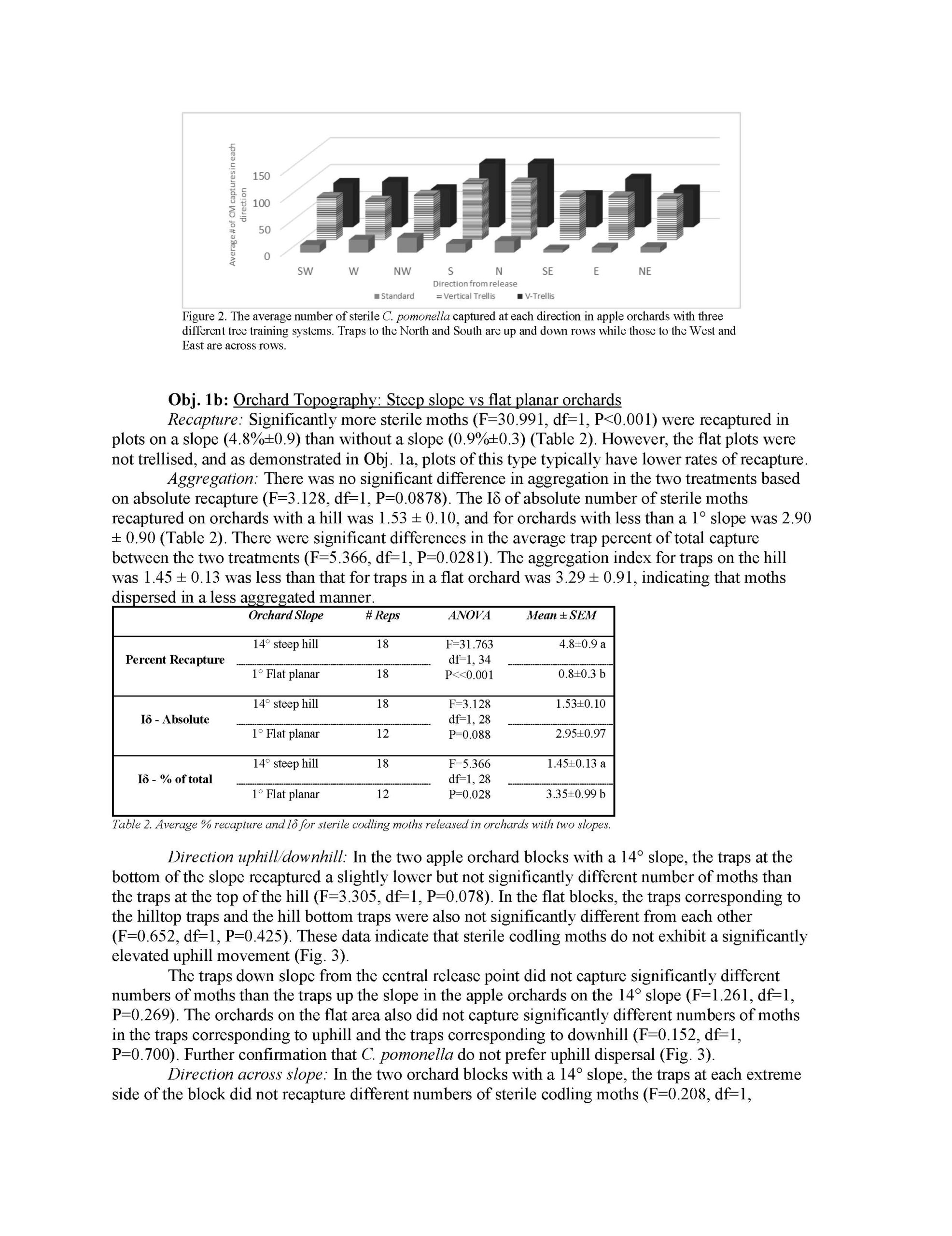
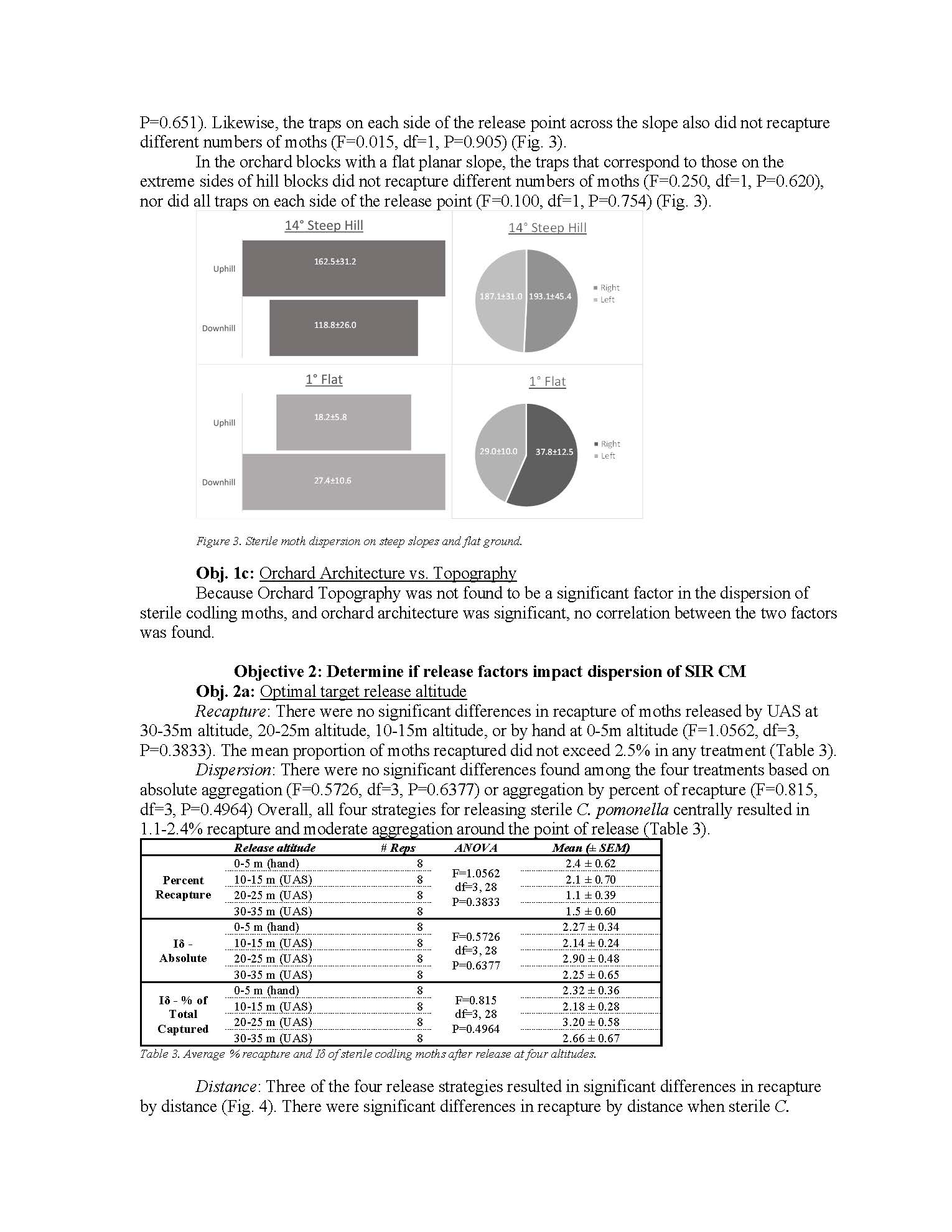
Optimization of release strategies for sterile codling moth
Author: Dr. Larry Gut (Posthumous)
Published: 2022
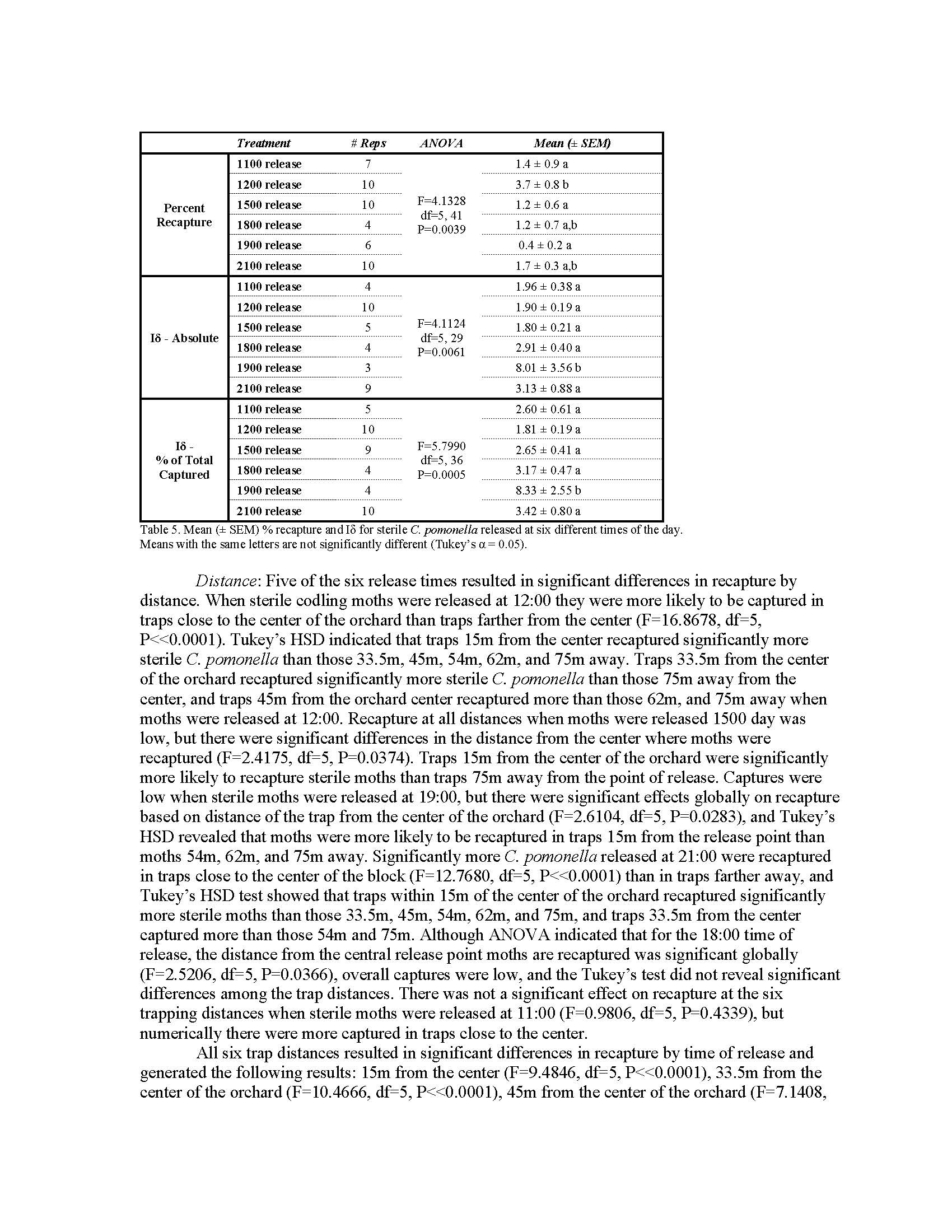
Summary: Sterile codling moth release as a control tactic recently became commercially available to Washington apple farmers. A better understanding of how released sterile codling moths behave on-farm in the presence of existing control tactics was necessary before this technology is recommended for adoption on an industry-wide scale. We studied how both factors inherent to modern orchards and factors that may be controlled at release impact dispersion and recapture of released sterile moths. We found that dispersion and recapture are impacted by orchard training systems, release locations, and release time of day, but not impacted by release altitude and orchard slopes. We demonstrate that sterile codling moth release is highly conducive to use in modern trellised orchards. Moths are flexible in the release and orchard conditions they will tolerate; they quickly distribute throughout the orchard when released at a single central location despite facing a variety of conditions. Based on the assumption that high moth recapture and slightly aggregated dispersion equates with effective on-farm control, we recommend use of a single central release location before noon in 10-ac trellised apple orchards. Unmanned aerial systems or hand releases are both effective tactics for deploying moths within orchards.
Keywords: